

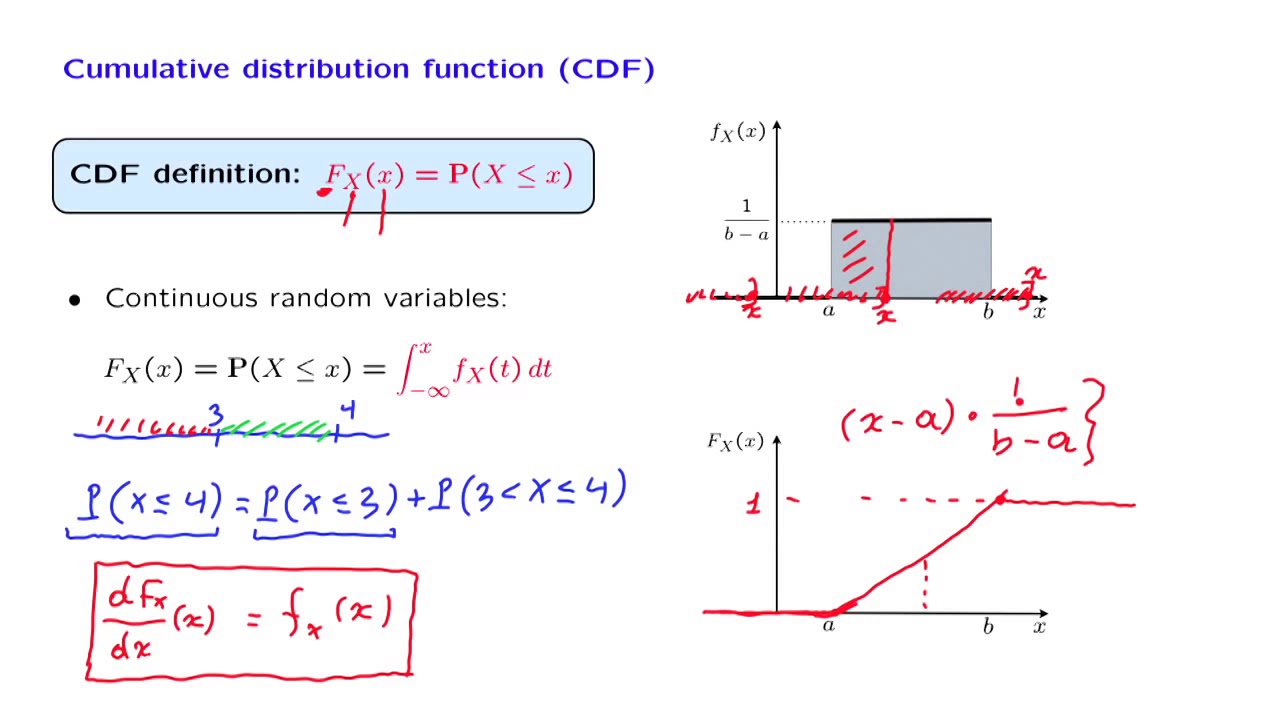

If I were to take a larger interval, and go up to some larger number y, this would be the probability of a bigger interval. įrom which the desired result (2.27) follows. So the CDF is, by definition, the probability of obtaining a value less than or equal to a certain number little x. temperature) and the y-axis the number of ENS members (expressed as a proportion of the total number. of temperature) for a given time and location, and consequently these results may be used to define a CDF where the x-axis is the forecast variable (e.g. Each member of the ENS gives a different forecast value (e.g. The following lemmas provide corresponding basic results for summations which arise with lattice RV probability calculations. Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) The Cumulative Distribution Function is the probability that a continuous random variable has a value less than or equal to a given value. Two of the most basic integrals we encounter are The value of h is called a span of the lattice RV. ThenĨ8 BASIC PROBABILITY THEORY FOR BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERS Let x be a discrete RV on the probability space (S, F, P ). The set of points D x for which the PMF is nonzero is called the support set for p x. Is called the probability mass function (PMF) for the discrete RV x. this process as a method of studying the nature of something or of determining its… … UniversaliumĬhemical bonding - ▪ chemistry Introduction any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules, ions, crystals, and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world.(a) To apply Theorem 2.2.1, we try to find an interval with inverse image not belonging to F. the separating of any material or abstract entity into its constituent elements (opposed to synthesis). Overview Evidenced based nursing/evidence based practice (EBN/EBP) is a nursing process that… … WikipediaĪnalysis - /euh nal euh sis/, n., pl. v.) the science that deals with the collection, classification, analysis, and interpretation of numerical facts or data, and that, by use of mathematical theories of probability, imposes order and… … Universaliumĭummy variable (statistics) - In statistics and econometrics, particularly in regression analysis, a dummy variable (also known as an indicator variable) is one that takes the values 0 or 1 to indicate the absence or presence of some categorical effect that may be expected to … WikipediaĮvidence-Based Nursing - or EBN is a method of identifying solid research findings and implementing them in nursing practices to further increase the quality of patient care.
Cdf probability pdf#
It includes both qualitative (comparative probability, partial preference… … WikipediaĬhi-square distribution - Probability distribution name =chi square type =density pdf cdf parameters =k > 0, degrees of freedom support =x in [0 +infty), pdf =frac(k 1/c, 1+1/c) where B() is the beta function median… … Wikipedia Imprecise probability - The notion of Imprecise probability is used as a generic term to cover all mathematical models which measure chance or uncertainty without sharp numerical probabilities. From such analyses measures can then be taken to… … Wikipedia Probabilities can be expressed as (i) *percentages, (ii) decimals between 0 and 1, (iii) fractions, and (iv)… … Auditor's dictionaryĪbsolute probability judgement - is a technique used in the field of human reliability assessment (HRA), for the purposes of evaluating the probability of a human error occurring throughout the completion of a specific task. Probability - The likelihood of the occurrence of an event, measured by the ratio of likely occurrences to the total number of possible occurrences. This differentiates it from quantitative analyzed for … Wikipedia Qualitative marketing research - is a set of research techniques, used in marketing and the social sciences, in which data is obtained from a relatively small group of respondents and not analyzed with inferential statistics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
